Understanding **CT Scans for Lung Cancer**
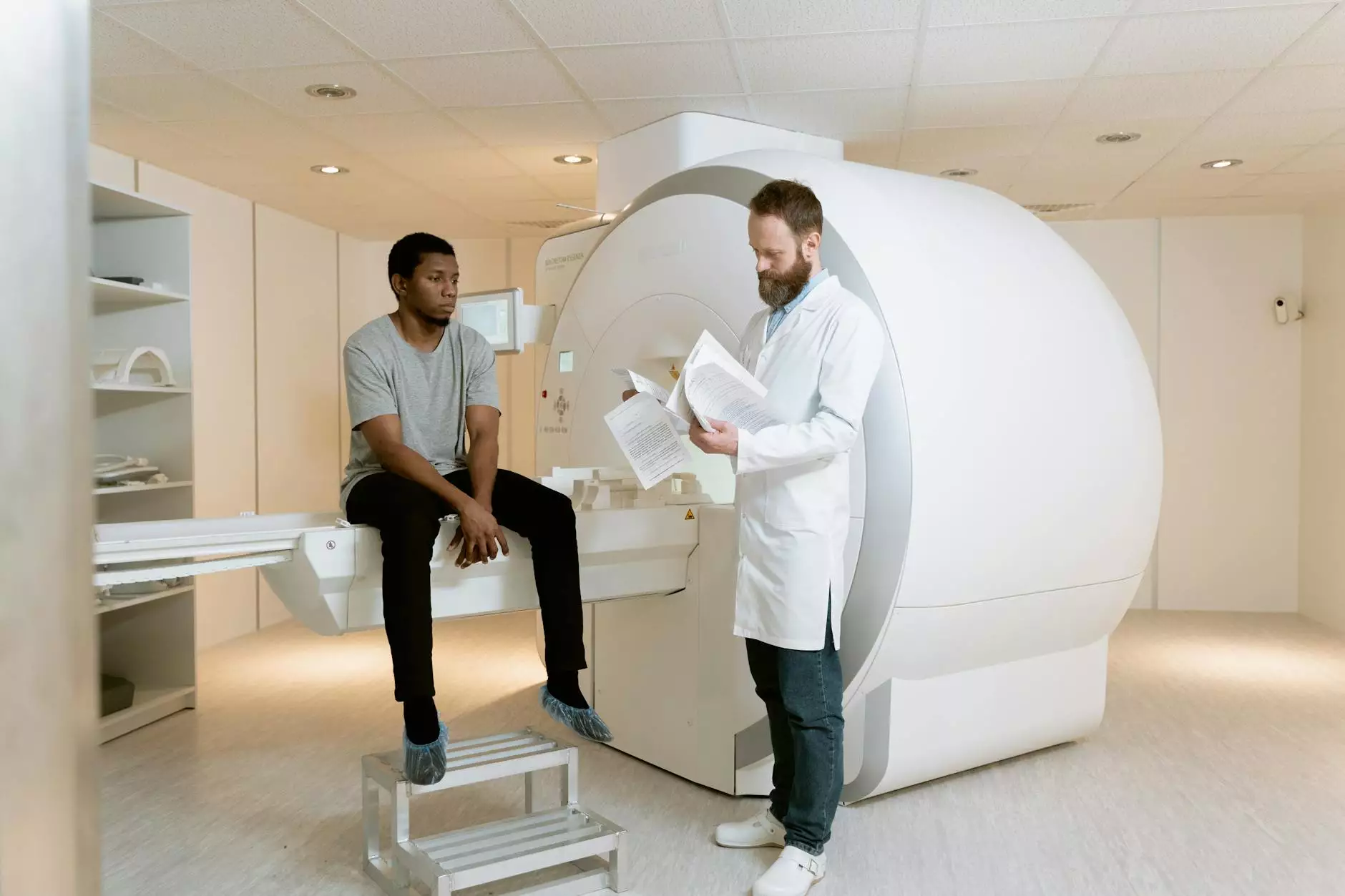
Lung cancer remains one of the most common and deadly cancers worldwide. Early detection significantly increases the chances of successful treatment and recovery. One of the most effective diagnostic tools used in the early detection of lung cancer is the CT scan (computed tomography scan). In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intricacies of CT scans for lung cancer, including their benefits, the procedure involved, and how they fit into the broader picture of healthcare.
What is a CT Scan?
A CT scan is a medical imaging technique that uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body, including the lungs. Unlike traditional X-rays, CT scans provide much clearer and more detailed images that allow healthcare providers to identify abnormalities more effectively.
How a CT Scan Works
The process begins with the patient lying on a table that slides into a large, doughnut-shaped machine. The machine emits a series of X-ray beams from different angles around the body, which are then processed by a computer to generate detailed images. These images can be viewed in multiple planes, offering a comprehensive look at the lung structure.
The Importance of CT Scans in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
CT scans for lung cancer have revolutionized how healthcare providers detect and monitor this disease. Here are several reasons why they are crucial:
- Early Detection: CT scans have a higher sensitivity in detecting early-stage lung cancer compared to conventional X-rays.
- Detailed Imaging: The high-resolution images allow for a better assessment of lung nodules and lesions.
- Guided Biopsies: CT imaging can help guide biopsies to ensure that samples are taken from the right areas.
- Monitoring Progress: CT scans are vital for monitoring existing lung cancer and evaluating treatment effectiveness.
Risk Factors and Recommended Screenings
Experts recommend annual CT scans for individuals who are at high risk for lung cancer, particularly those who:
- Are aged 55 to 80 years.
- Have a significant smoking history (30 pack-years or more).
- Are current smokers or have quit within the last 15 years.
Preparing for a CT Scan for Lung Cancer
Preparation can enhance the accuracy of a CT scan for lung cancer. Here are common steps patients may need to follow:
- Discuss Medical History: Inform your doctor about any medications, allergies, or previous reactions to contrast materials.
- Fast if Necessary: You may be asked to refrain from eating or drinking for a few hours before the scan.
- Wear Comfortable Clothing: Dress in clothes without metal zippers or buttons that could interfere with imaging.
The CT Scan Procedure
The procedure typically lasts between 10 to 30 minutes, and most people find it painless. During the scan:
- You will be positioned on your back on the examination table.
- The technician will guide you on how to hold your breath at certain points to minimize movement.
- If contrast dye is used, it may be injected via an IV to highlight blood vessels and improve image clarity.
Post-Scan Process
After the CT scan for lung cancer, you can usually return to your normal activities immediately unless advised otherwise. If contrast was used, hydration is encouraged to help flush the dye out of your system.
Interpreting CT Scan Results
The results of a CT scan are typically reviewed by a radiologist, who will prepare a report for your doctor. The report will include:
- Findings: Any observed nodules, masses, or other abnormalities.
- Recommendations: Further testing or monitoring if necessary.
Common Findings on Lung CT Scans
While most lung nodules are benign, some findings can be indicative of lung cancer. These may include:
- Size: Nodules larger than 3 cm are more likely to be cancerous.
- Shape: Irregularly shaped nodules may raise suspicion.
- Growth Rate: Comparison with previous scans can indicate if a nodule is growing rapidly.
Limitations of CT Scans for Lung Cancer
While CT scans are a powerful tool, they are not without limitations:
- False Positives: CT scans may identify non-cancerous nodules that could lead to unnecessary biopsies and anxiety.
- Radiation Exposure: CT scans involve exposure to radiation, though the benefits often outweigh the risks in high-risk patients.
Conclusion: The Role of CT Scans in the Future of Lung Cancer Diagnosis
As technology continues to advance, CT scans for lung cancer are becoming more refined, improving the accuracy of lung cancer detection. Ongoing research and development in imaging technology promise to enhance the diagnostic capabilities of CT scans even further, potentially allowing for earlier detection and better patient outcomes.
For individuals at risk for lung cancer, understanding the significance of CT scans can empower them to take proactive steps in their health care journey. With early detection, timely intervention, and appropriate treatments, the prognosis for lung cancer patients can improve significantly.
Consulting with Healthcare Professionals
If you have concerns about lung cancer or are at risk, consult with esteemed health professionals. Organizations such as Hello Physio provide valuable resources in Health & Medical services, Sports Medicine, and Physical Therapy. They are equipped to guide you in understanding the role of CT scans and other critical diagnostic processes in managing lung health.